Plant-Based Diets: How to Ensure Balanced Nutrition

Plant-based diets have grown in popularity in recent years due to their potential health benefits, environmental sustainability, and ethical considerations. Whether you're fully vegan, vegetarian, or just looking to eat more plant-based meals, transitioning to a plant-based diet can be an excellent choice for improving your overall health. However, like any diet, it's important to ensure that it is well-balanced and provides all the essential nutrients your body needs to thrive.
There’s no single way to eat plant-based, and that’s part of its strength. Some people follow a vegan diet, avoiding all animal-derived products including meat, dairy, eggs, and even honey. Others choose a vegetarian diet, which excludes meat and fish but may still include dairy and eggs. Then there are those who eat a primarily plant-based diet, focusing on whole plant foods while still including small amounts of animal products like fish, eggs, or dairy. Whether you’re fully plant-based or simply shifting towards more plant-forward meals, the key is to make your choices intentional, inclusive of diverse foods, and aligned with your health goals and values!
This article will explore how to ensure balanced nutrition while following a plant-based diet, covering key nutrients to be mindful of, the best plant-based food sources for those nutrients, and practical tips for building a nutrient-rich plant-based meal plan.
Why Choose a Plant-Based Diet?
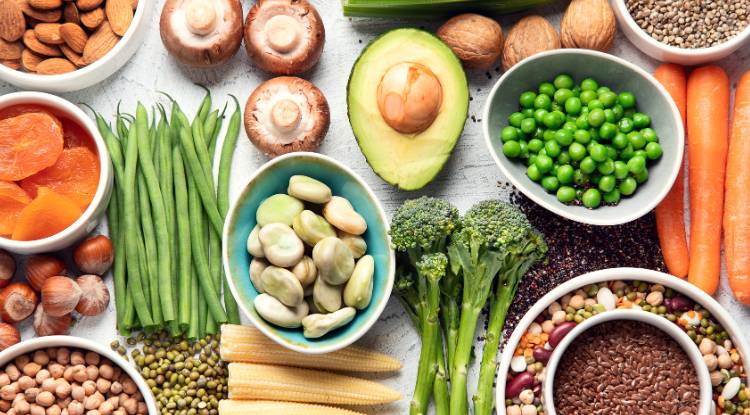
A plant-based diet emphasises foods derived primarily from plants, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, and plant-based protein sources. Many people choose a plant-based diet for reasons such as:
Health Benefits: Studies have shown that plant-based diets can lower the risk of chronic diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. They are typically rich in fiber, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals while being lower in saturated fat.
Weight Management: A plant-based diet can support healthy weight loss and maintenance due to its high fiber content, which promotes satiety and reduces calorie intake.
Environmental Impact: Plant-based diets are more sustainable, requiring fewer resources (such as water and land) and producing fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to animal-based food production.
Ethical Considerations: For many, a plant-based diet aligns with ethical values regarding animal welfare and the desire to reduce animal suffering.
Key Nutrients to Consider on a Plant-Based Diet
While a plant-based diet can be nutritionally complete, certain nutrients may be more challenging to obtain in adequate amounts, and some, like vitamin B12, will need to be supplemented. It's important to be aware of these nutrients and find reliable plant-based sources or supplements to meet your needs. Let’s explore the essential nutrients to focus on when following a plant-based diet.
Protein
Protein is a critical nutrient for muscle repair, immune function, and the production of enzymes and hormones. While animal-based foods are often considered the gold standard for protein, many plant-based foods are also rich in protein. The key is to eat a variety of plant-based protein sources to ensure you get all the essential amino acids your body needs.
Plant-Based Protein Sources:
Legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas)
Tofu and tempeh (made from soy)
Edamame
Seitan (wheat gluten)
Quorn (mycoprotein)
By incorporating a mix of these protein-rich foods into your meals, you can easily meet your protein requirements.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin that is crucial for nerve function, red blood cell production, and DNA synthesis. It is found naturally only in animal products, so vegans and strict vegetarians must pay attention to B12 intake. Deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to anemia, neurological damage, and cognitive issues.
Plant-Based Sources of B12:
Fortified plant-based milks (soy, almond, oat milk)
Fortified breakfast cereals
Nutritional yeast (often used as a cheese substitute)
B12 supplements (recommended for vegans and vegetarians)
It’s advisable to have your vitamin B12 levels monitored regularly and consider taking a B12 supplement if needed.
Iron
Iron is essential for oxygen transport in the blood, energy production, and overall cellular function. While plant-based iron (non-heme iron) is less readily absorbed by the body compared to animal-based iron (heme iron), you can still meet your iron needs with careful food choices.
Plant-Based Iron Sources:
Lentils, beans, and chickpeas
Tofu and tempeh
Quinoa
Spinach and other dark leafy greens
Pumpkin seeds and sesame seeds
Dried fruits (apricots, raisins, figs)
To improve iron absorption from plant-based sources, pair iron-rich foods with vitamin C-rich foods like citrus fruits, bell peppers, or broccoli, as vitamin C enhances non-heme iron absorption.
Calcium
Calcium is vital for bone health, muscle function, and nerve transmission. While dairy products are often considered the main source of calcium, there are plenty of plant-based options available. It's important to consume enough calcium to support bone density and reduce the risk of osteoporosis later in life.
Plant-Based Calcium Sources:
Fortified plant-based milks (soy, almond, oat milk)
Leafy greens (collard greens, bok choy, kale)
Broccoli
Almonds and tahini
Fortified tofu
Chia seeds and sesame seeds
If you’re concerned about calcium intake, consider fortified foods and speak to a healthcare provider or nutritionist for guidance.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D plays a crucial role in calcium absorption and bone health. It also supports the immune system and reduces inflammation. While vitamin D can be synthesised through sunlight exposure, it can be more difficult to obtain adequate amounts from food alone, especially in certain climates or during winter months.
Plant-Based Sources of Vitamin D:
Fortified plant-based milks
Fortified cereals
Mushrooms exposed to sunlight (shiitake, maitake)
Vitamin D supplements (vegan D3 derived from lichen)
If you live in a region with limited sunlight, a vitamin D supplement may be necessary to maintain optimal levels.
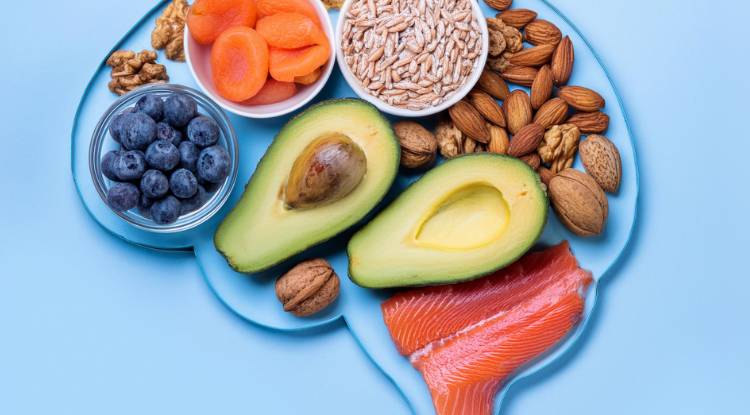
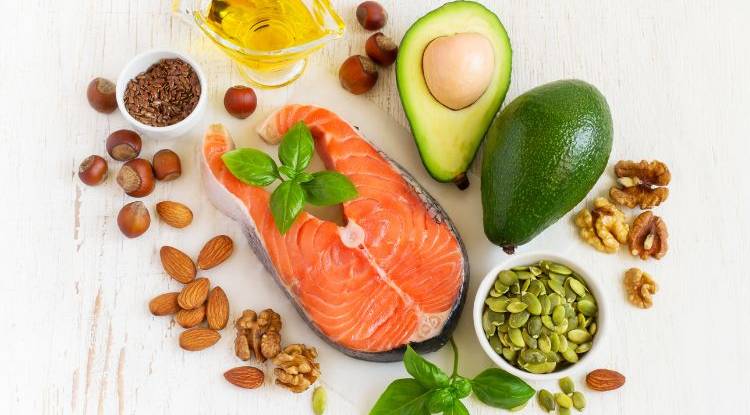
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that support brain health, heart health, and reduce inflammation. Omega-3s are primarily found in fatty fish, but there are several plant-based sources that provide the necessary building blocks for omega-3s.
Plant-Based Omega-3 Sources:
Chia seeds
Flaxseeds and flaxseed oil
Walnuts
Hemp seeds
Algal oil (plant-based DHA and EPA supplements)
To support your omega-3 intake, regularly include chia seeds, flaxseeds and walnuts in your meals. These plant-based sources provide ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), which is a precursor to EPA and DHA, the forms your body uses most efficiently.
However, since the conversion of ALA to EPA and DHA is limited, it’s strongly recommended to consider a high-quality algae-based omega-3 supplement. This provides a direct source of EPA and DHA and ensures your brain, heart and cells receive the essential fats they need, especially if you follow a plant-based or low-fish diet.
Zinc
Zinc is essential for immune function, wound healing, DNA synthesis, and cell division. It is more abundant in animal products, but there are plant-based sources that can help meet your needs.
Plant-Based Zinc Sources:
Legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas)
Whole grains (oats, quinoa, brown rice)
Nuts and seeds (pumpkin seeds, cashews)
Tofu and tempeh
Fortified breakfast cereals
Quorn (mycoprotein)
Iodine
Iodine is necessary for thyroid function and regulating metabolism. While iodine is typically found in dairy, eggs, and seafood, vegans may be at risk for deficiency unless they consume iodine-rich plant-based foods or iodised salt.
Plant-Based Iodine Sources:
Seaweed (nori, kelp, wakame)
Iodised salt
Make sure to consume seaweed in moderation, as excess iodine can also be harmful.
Tips for Ensuring Balanced Plant-Based Nutrition
To ensure you’re meeting your nutritional needs on a plant-based diet, consider the following tips:
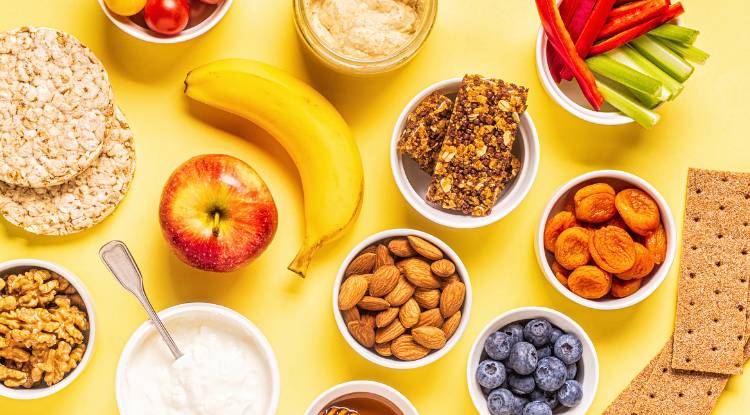
Eat a Variety of Foods: Consuming a wide variety of fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and fortified foods ensures that you get a broad spectrum of nutrients.
Plan Your Meals: Proper planning is key to a balanced plant-based diet. Ensure each meal contains a variety of food groups, including protein, healthy fats, complex carbohydrates, and plenty of fiber-rich vegetables.
Supplement Wisely: Some nutrients may require supplementation, such as vitamin B12, vitamin D, and omega-3s. Speak with a healthcare professional to determine if and which supplements are necessary for you.
Keep an Eye on Your Intake: When transitioning to a plant-based diet, it can be helpful to use a food journal or nutrition app to track your meals. This isn’t about perfection, but about building awareness, it can highlight whether you're consistently meeting your needs for key nutrients or reveal areas that may need more attention.
Limit Reliance on Ultra-Processed Vegan Foods: While convenient, many plant-based alternatives like vegan cheeses, sausages, and ready meals can be high in salt, saturated fats, and additives, yet low in essential nutrients. These products can be enjoyed occasionally, but prioritise building your meals around whole plant foods
Stay Hydrated: Water is essential for digestion and overall health, so make sure you’re drinking plenty of water throughout the day, especially if you’re consuming a high-fiber diet.
Consult a Nutritionist or Dietitian: If you’re new to a plant-based diet or have specific dietary concerns, consider consulting a registered nutritionist or dietitian with expertise in plant-based nutrition. They can provide personalised guidance and help you avoid potential deficiencies.
Conclusion
A plant-based diet can be an incredibly healthful and sustainable choice, but it requires thoughtful planning to ensure balanced nutrition. By paying attention to key nutrients like protein, vitamin B12, iron, calcium, omega-3s, and others, you can enjoy the many benefits of a plant-based diet while maintaining optimal health. With a little preparation and knowledge, you can easily build a nutrient-dense, satisfying plant-based eating plan that supports both your health and well-being.
Simply Supplements offers a range of expertly formulated products that can support key nutrients often harder to obtain through a fully plant-based diet, helping you stay nourished, balanced and confident in your choices.
Sources:
https://www.bda.uk.com/resource/vegetarian-vegan-plant-based-diet.html
https://www.bda.uk.com/resource/plant-based-eating-for-beginners.html
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5466942/
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7613518/

 Funmi Akinola (Msc, Anutr)
Funmi Akinola (Msc, Anutr)